Odoo 18 introduces refined tools for managing search functionalities, making data retrieval more efficient. This guide will walk you through configuring search views, filters, and grouping options to enhance user experience and streamline workflows. Mastering these techniques can significantly improve productivity by enabling users to find relevant data faster and with greater accuracy.
This blog will guide you through the process of configuring search views, filters, and groupings in Odoo 18.
Defining a Search View in Odoo 18
A search view helps users locate relevant records quickly by allowing specific search criteria. In Odoo, search views are defined using XML within the module’s views folder. Customizing search views can make data exploration more user-friendly and efficient.
Example XML Code:
<record id="custom_search_view" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">Custom Search</field>
<field name="model">your.model.name</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<search>
<field name="name"/>
<field name="email"/>
</search>
</field>
</record>
Explanation:
- The <search> tag defines the search structure.
- The <field> elements specify which fields are searchable.
- Users can input queries based on these fields, allowing Odoo to filter results efficiently.
- Additional fields can be added based on business needs.
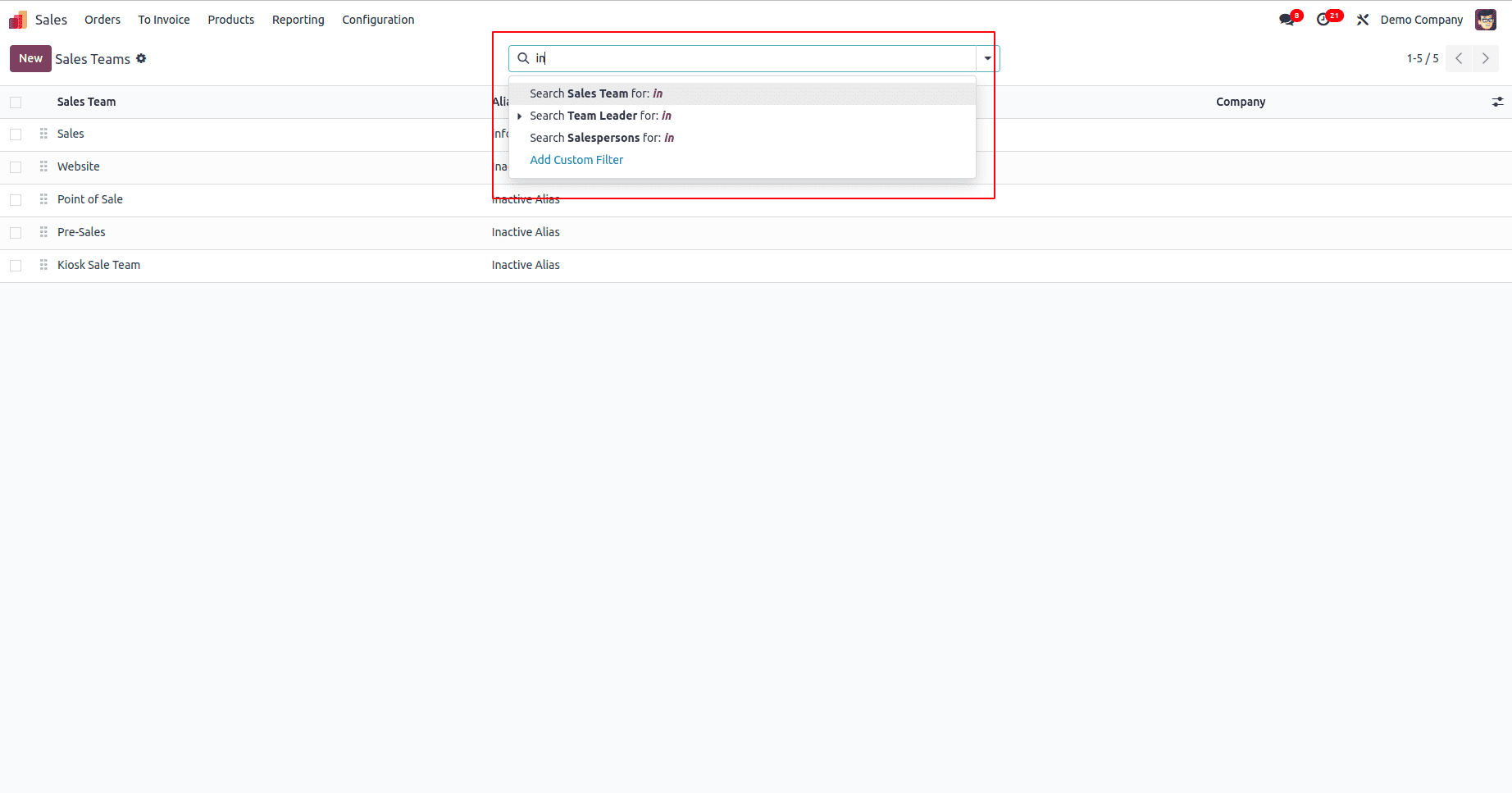
This image showcases how the search view appears in the Odoo user interface after configuration.
Best Practices for Search Views
- Keep search fields relevant to user needs.
- Avoid adding too many fields, as this can clutter the search interface.
- Use meaningful field labels that align with user expectations.
Search views enhance navigation and data retrieval by ensuring users can locate information without sifting through unnecessary records. The flexibility of the search view allows administrators to fine-tune it based on business requirements.
Implementing Filters in Search Views
Filters refine search results by applying predefined conditions. They help users quickly identify records that match specific attributes. Filters can be especially useful when working with large datasets, as they allow users to focus only on relevant data.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<record id="search_view_with_filter" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">Custom Search with Filter</field>
<field name="model">your.model.name</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<search>
<field name="field1"/>
<field name="field2"/>
<filter string="Inactive" name="inactive_filter" domain="[('active', '=', False)]"/>
</search>
</field>
</record>
Explanation:
- The <filter> tag creates a custom filter.
- The string attribute specifies the label for the filter.
- The domain condition filters records where the active field is False.
- Users can enable this filter to view inactive records without entering a manual search query.
- Multiple filters can be defined to refine searches based on different parameters.
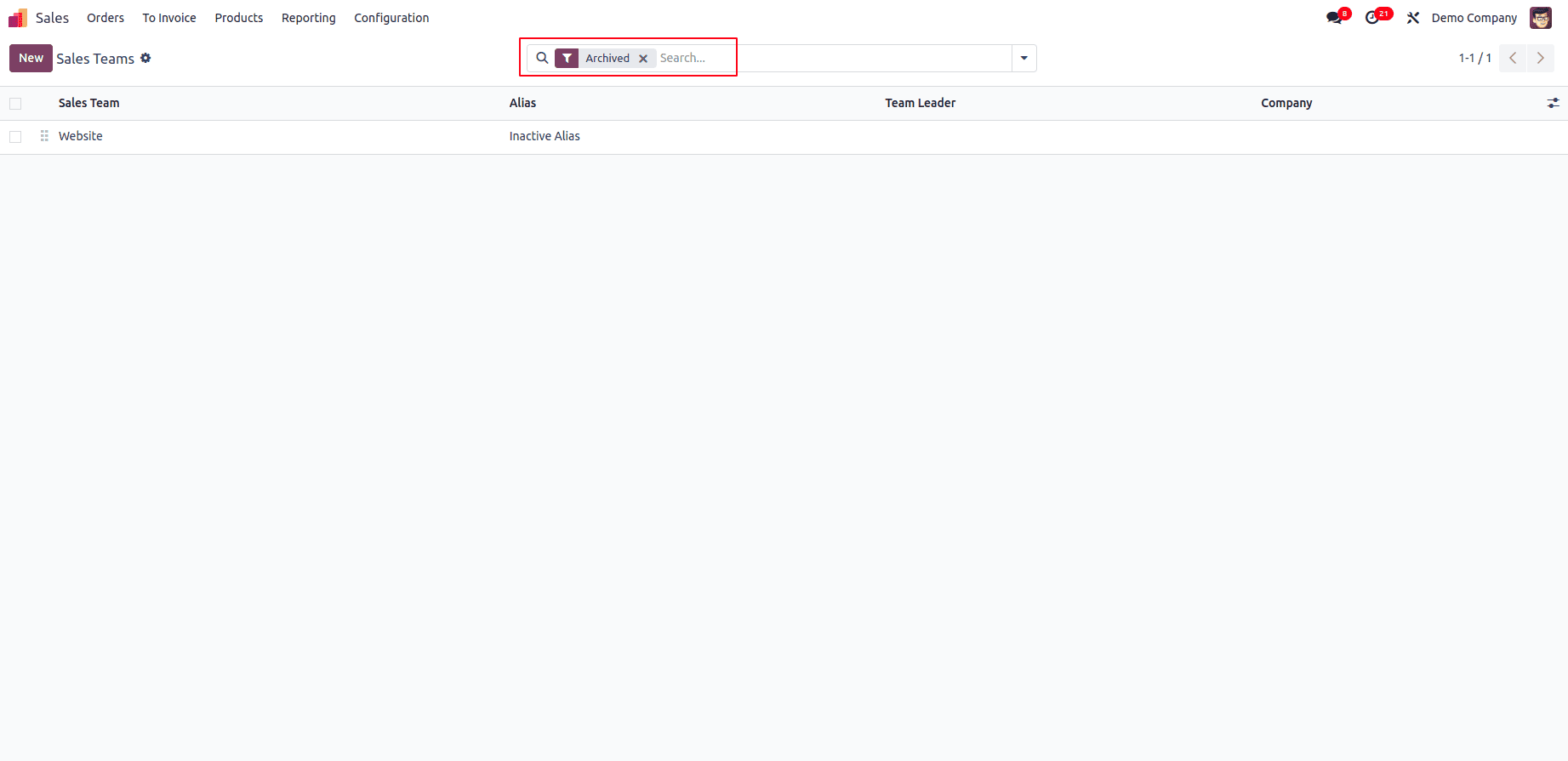
This image demonstrates how the filter appears in the Odoo UI, allowing users to refine their search.
Filters in search views make navigation seamless and allow users to quickly apply frequently used conditions. Well-configured filters can improve data accuracy and prevent unnecessary manual searching.
Advanced Filter Techniques
- Relative Date Filters: Allow filtering based on dynamic date ranges such as "Last 30 Days."
- Boolean Filters: Enable quick toggling of attributes like "Show Active Users."
- Multi-Condition Filters: Combine multiple conditions, such as "Customers with Overdue Payments."
Grouping Records for Better Organization
Grouping helps categorize data for easier analysis. Odoo’s search views support grouping by specific fields, allowing users to organize records efficiently. Grouping enhances clarity and helps in better visual representation of data.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<record id="search_view_with_group" model="ir.ui.view">
<field name="name">Search View with Grouping</field>
<field name="model">your.model.name</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<search>
<field name="name"/>
<field name="email"/>
<filter string="Inactive" name="inactive_filter" domain="[('active', '=', False)]"/>
<group expand="0" string="Group By">
<filter string="Company" name="company_group" context="{'group_by': 'company_id'}"/>
</group>
</search>
</field>
</record>
Explanation:
- The <group> tag enables grouping functionality.
- The expand="0" attribute ensures the groups are collapsed by default.
- The context attribute instructs Odoo to group records based on company_id.
- Additional groupings can be added based on various fields to improve data visualization.
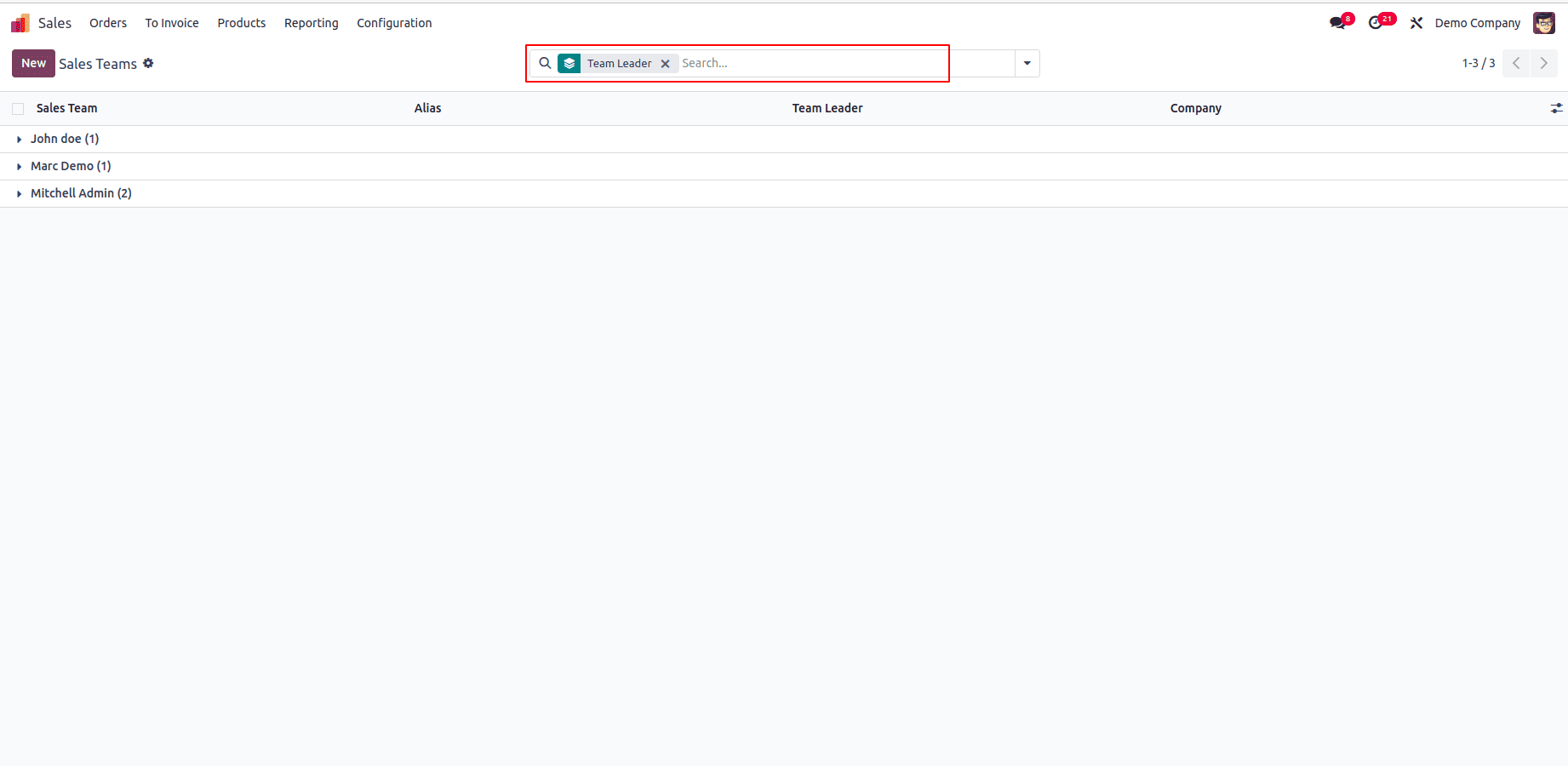
This image shows how records are displayed in the Odoo UI when grouped by Team Leader.
Grouping options provide structured data presentation, making it easier to analyze records based on different categories.
Real-World Use Cases for Grouping
- Grouping by Salesperson: Helps track individual sales performance.
- Grouping by Status: Easily manage records by status, such as "Pending," "Completed," or "Canceled."
- Grouping by Region: Organize customers or orders based on geographic location.
Configuring search views, filters, and group by options in Odoo 18 enhances the way users interact with data. By defining structured search parameters, applying efficient filters, and utilizing grouping techniques, businesses can streamline operations and improve productivity. Additionally, Odoo’s advanced search enhancements make data exploration more intuitive and powerful.
Implement these configurations in your Odoo environment to provide users with an optimized and seamless search experience. By customizing search views, filters, and group options, you can significantly boost the efficiency of your Odoo workflows, ensuring users can access relevant data with ease.
To read more about How to Configure Search View, Filter & Group by in Odoo 17, refer to our blog How to Configure Search View, Filter & Group by in Odoo 17